As urbanization in Asia surges, the need for sustainable, eco-friendly skyscrapers has never been more urgent. Siemens, a global leader in technology and sustainable engineering, has been instrumental in pioneering high-performance buildings across Asia. With projects that meet the stringent requirements for LEED certification, Siemens has set new standards for energy efficiency, resource management, and indoor environmental quality in high-rise structures, showcasing the future of sustainable urban development.
The DEGREE Framework and Siemens’ Commitment to Sustainability
At the heart of Siemens’ engineering strategy is the DEGREE framework, a comprehensive approach that prioritizes decarbonization, resource efficiency, and circular economy principles. This commitment is realized through Siemens Global Business Services (GBS) Engineering, which leverages extensive expertise in mechanical, electrical, and civil engineering to deliver energy-efficient solutions for buildings worldwide. Siemens’ mission to lead in sustainable solutions is exemplified in the skyscrapers it has helped engineer across Asia, demonstrating how cutting-edge technology can meet environmental goals without compromising on performance.

Sustainable Initiatives Powering High-Rise Design
Siemens’ approach to sustainable high-rises focuses on advanced building management and the integration of energy-efficient systems. Central to their design philosophy is reducing operational energy demands through integrated digitalization and automation. Their Building Management Systems (BMS) intelligently control HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, and shading, adapting these systems based on real-time data to reduce energy consumption significantly. This setup provides a reliable infrastructure that can be remotely managed and monitored, optimizing energy use while enhancing occupant comfort.
Another groundbreaking initiative by Siemens is the implementation of digital twins—a virtual representation of a building that monitors and simulates real-time conditions. By predicting and managing energy requirements, these digital replicas enable building managers to identify inefficiencies and make informed decisions that reduce carbon emissions. For skyscrapers in Asia, the digital twin approach has been transformative, allowing developers to test sustainable designs before implementation and adapt these virtual models as buildings operate.
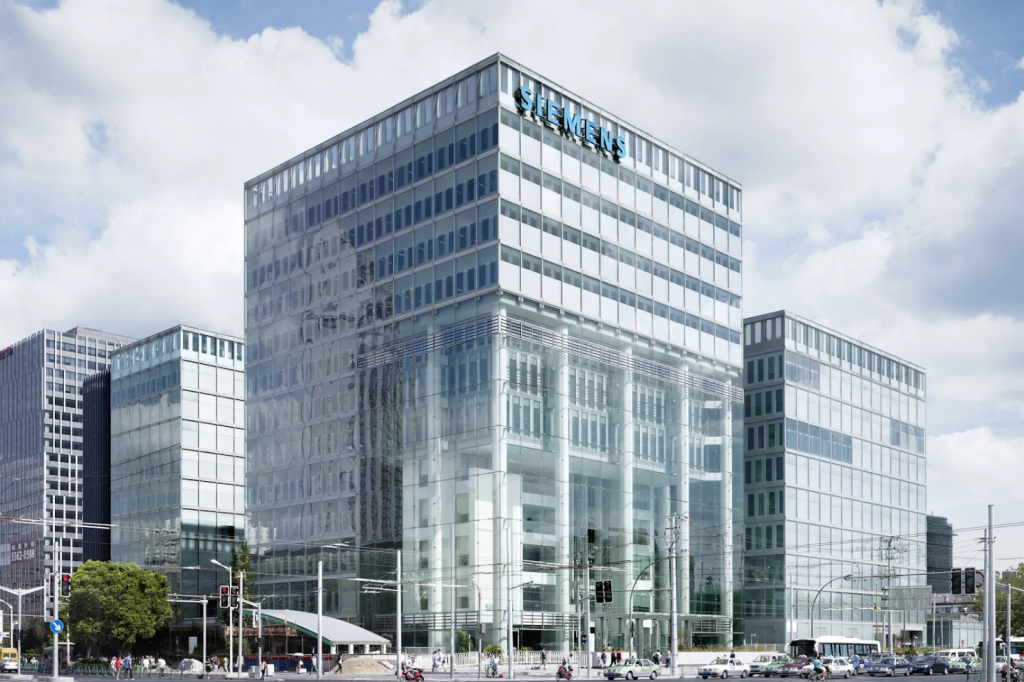
Case Study: Siemens Center in Shanghai
A landmark example of Siemens’ impact is the Siemens Center in Shanghai. Designed with a suite of sustainable technologies, this high-rise achieved LEED Gold certification, an acknowledgment of its minimal environmental impact and superior energy efficiency. The building operates with 30% less energy than the average commercial structure in China, incorporating a high-efficiency BMS that monitors and controls water and energy use. The building’s rainwater harvesting system and water-efficient fixtures further minimize resource use, addressing the critical need for water conservation in rapidly urbanizing cities.
This Shanghai project demonstrates how Siemens’ advanced engineering not only meets sustainability criteria but also adapts to local environmental demands. Through features like optimized lighting controls, temperature management, and high-performance insulation, Siemens Center stands as a beacon of green architecture, offering a replicable model for other cities in Asia.

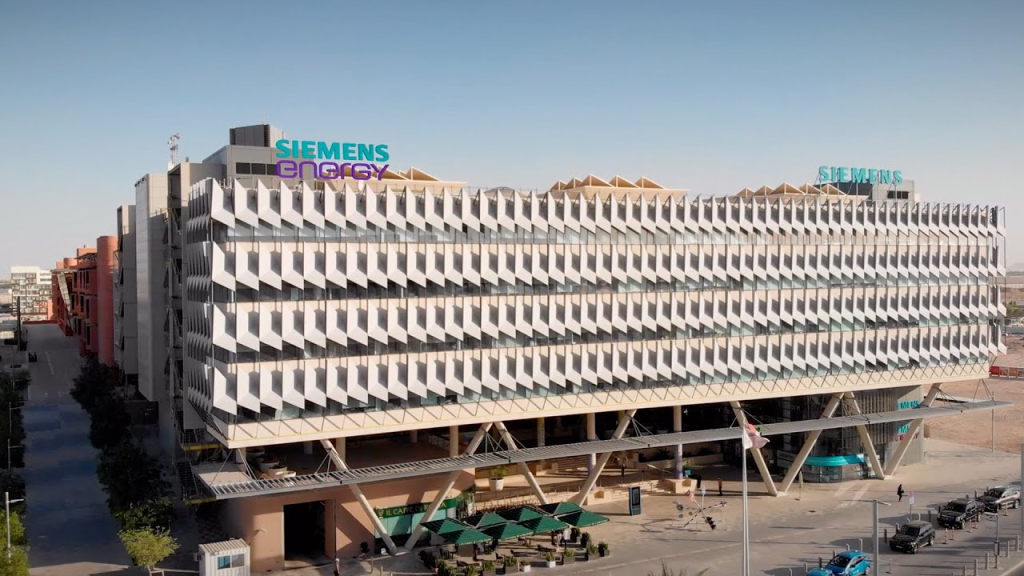
Pioneering LEED Platinum in Abu Dhabi’s Masdar City
Siemens’ commitment to green architecture is also evident in the Middle East, where its regional headquarters at Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, became the first LEED Platinum-certified building in the UAE capital. The building’s design is tailored to reduce thermal conductivity through a “box-within-a-box” structure, which maximizes natural daylight while minimizing heat intake. This innovative setup not only enhances energy efficiency by nearly 50% compared to conventional office buildings but also fosters a comfortable indoor climate with reduced reliance on artificial lighting and air conditioning.
By combining cutting-edge insulation with a unique shading system, Siemens achieved an ideal balance of aesthetics, energy savings, and sustainable functionality. Such advancements underscore the scalability of Siemens’ engineering solutions, highlighting how they can be adapted across varied climates and architectural styles, from temperate urban centers in Asia to the arid environment of the Middle East.

LEED-Certified Skyscrapers: A Testament to Siemens’ Success
One of the most impressive examples of Siemens’ sustainable engineering is a skyscraper in Asia striving for top-tier LEED certification. Through Siemens’ work on the building’s BMS and graphic visualization, the high-rise achieved a significant reduction in energy and water consumption, meeting stringent LEED criteria for indoor environmental quality. This success story is not isolated—Siemens’ contributions to eco-friendly high-rises extend across many countries, helping transform urban landscapes while promoting environmental stewardship.
Siemens has also been instrumental in projects such as data centers, known for their high energy demands. Through extensive energy monitoring and central performance control, Siemens has helped reduce energy consumption significantly, setting a new standard for sustainable data infrastructure.
The Future of High-Rise Sustainability in Asia
As Asia’s cities continue to grow, Siemens’ contributions to LEED-certified high-rises provide a blueprint for sustainable urbanization. The combination of advanced digital solutions, efficient engineering services, and commitment to environmental sustainability positions Siemens as a pivotal player in shaping the green skyscrapers of tomorrow. These projects are more than technological feats; they reflect a vision where engineering, sustainability, and quality of life intersect seamlessly, making urban spaces healthier, more sustainable, and more resilient.
Siemens’ sustainable high-rise projects illustrate the potential of engineering excellence in tackling environmental challenges. Through innovations like digital twins, BMS optimization, and long-lasting product designs, Siemens is leading the charge towards a future where skyscrapers contribute positively to their environments. With its expertise, Siemens is poised to drive a new era of urban development—one where buildings not only house people but also safeguard the planet.


