Reducing Global Carbon Emissions with Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3)
Concrete is the second most consumed substance globally, with an annual consumption rate of 30 billion tons. Cement, a crucial component of concrete, is responsible for approximately 90 percent of the emissions associated with concrete production. Furthermore, it contributes to 8 percent of global anthropogenic CO2 emissions.
As the demand for cement continues to grow on a global scale, addressing these emissions is essential. Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) has emerged as a climate-friendly innovative solution to reduce carbon emissions associated with cement production. In this blog post, we explore the potential of LC3 as a global solution for carbon emission reduction and the implications of recent developments.
LC3 as a Replacement for Conventional Cement
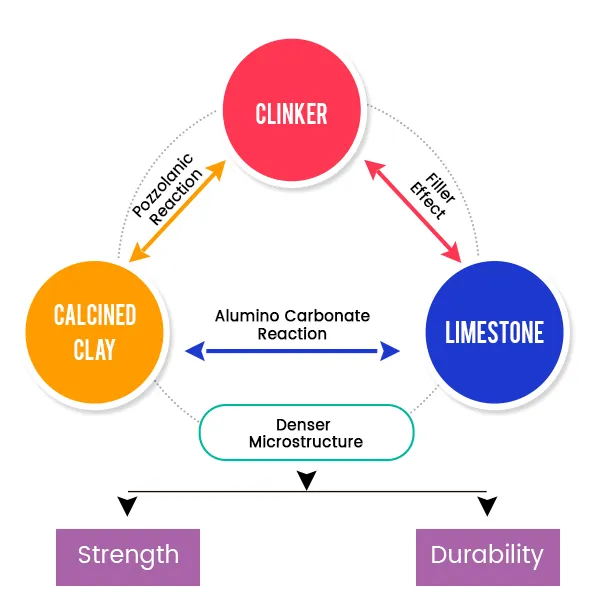
Developed as a low-carbon alternative to Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), LC3 is a promising innovation. Traditional cement relies on an ingredient called Clinker which is highly carbon intensive. LC3 has a change to that as it has replaced half the Clinker with Calcined Clay and ground Limestone. A typical LC3-50 cement blend consists of 30 percent calcined clay, 15 percent limestone, 5 percent gypsum, and 50 percent clinker. This composition results in a significant reduction of carbon emissions, with LC3 achieving up to 40 percent fewer emissions compared to OPC. Additionally, LC3 offers cost savings of up to 25 percent, making it an economically viable choice.
Research conducted in India has highlighted the improved durability characteristics of LC3, it doesn’t release much Carbon when heated, can be fired at much lower temperatures, less vulnerable to water & salt, making it suitable for various construction applications. Its enhanced resistance to chloride ingress and sulfate attack makes it an excellent option for structures located in coastal areas. Furthermore, LC3 has a lower alkali content, reducing the risk of alkali-silica reactions and enhancing the longevity of concrete structures.
Deployment Around the Globe
LC3 has transitioned from a research project to large-scale deployment on a global scale. This shift is driven by the growing awareness of climate change and the need for more sustainable construction practices. As the availability of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) like fly ash and slag decreases globally, LC3 becomes a promising alternative. Deploying LC3 is pretty much viable as it is scalable as it depends on the existing equipment for manufacture.
Examples of LC3 deployment around the world include:

1. Cuba In 2020, Cuba installed an LC3 pilot production plant, with plans to construct over 20 smaller plants. These plants will produce a clay mixture that can be blended with regular cement directly at construction sites, leading to an estimated 20 percent cost reduction. 2. Colombia Cementos Argos completed a new calcined clay production line in 2020 with a capacity of 450,000 tons per year. 3. Ghana CBI Ghana’s Accra plant is set to become the largest LC3 production facility globally by the second half of 2024. 4. Malawi Lafarge Cement Malawi launched an LC3 project in 2022, showcasing the growing adoption of this innovative technology in the region. 5. Europe Holcim introduced a calcined clay cement operation in France, offering ECOPlanet green cement with a 50 percent lower CO2 footprint compared to standard cement. Cementir Group’s FUTURECEM, another calcined clay cement product, debuted in Denmark in 2021.
Future Outlook of LC3 on a Global Scale
As the world grapples with reducing carbon emissions, LC3 presents a promising solution for low-carbon construction. Several barriers to its widespread deployment, such as raising awareness, ensuring consistent quality control, specialized training, and integrating LC3 into existing supply chains, must be addressed. However, with LC3’s reduced carbon footprint, improved durability, and economic benefits, it has the potential to transform the global construction industry. LC3 represents a promising and innovative solution to reduce carbon emissions in the cement industry. As a replacement for traditional cement, it offers environmental benefits, cost savings, and enhanced durability. The global deployment of LC3 in various countries, including Cuba, Colombia, Ghana, and Europe, demonstrates its potential to revolutionize the construction industry worldwide.


