In recent years, global temperatures have surged, igniting widespread concern among scientists, policymakers, and the public. The implications of this warming trend are dire, with far-reaching consequences for ecosystems, food security, and natural disasters. The ramifications of rising temperatures are profound and demand urgent attention.
The extra heat is driving regional and seasonal temperature extremes, reducing snow cover and sea ice, intensifying heavy rainfall, and changing habitat ranges for plants and animals—expanding some and shrinking others.
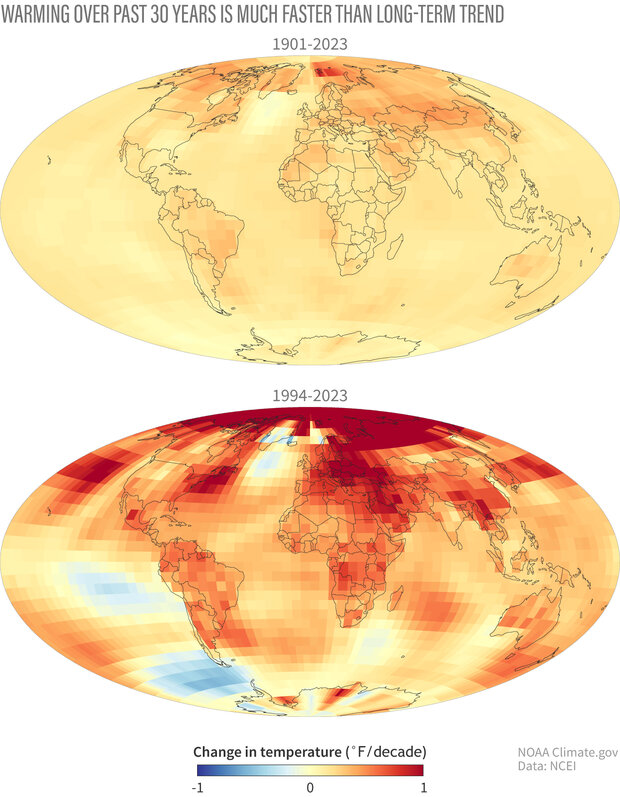
The Magnitude of Change in Global Temperature
According to an ongoing temperature analysis led by scientists at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS), since 1880, the Earth’s average temperature has increased by at least 1.1°C (1.9°F), predominantly due to human-induced climate change. This trend has accelerated since 1975, with 2023 marking the warmest year on record. Projections indicate further warming, with temperatures expected to rise by 1.5°C (2.7°F) by 2050 and 2-4°C (3.6-7.2°F) by 2100.
THE 10 WARMEST YEARS IN THE HISTORICAL RECORD HAVE ALL OCCURRED IN THE PAST DECADE (2014-2023)
Global Temperature in 2023
According to the 2023 Global Climate Report from NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, every month of 2023 ranked among the 7 warmest for that month, and the months in the second half of the year (June-December) were each the hottest on record. In July, August, and September, global temperatures were more than 1.0°C (1.8°F) above the long-term average—the first time in NOAA’s record any month has breached that threshold.
The Human Toll
Air temperatures on Earth have been rising since the Industrial Revolution. While natural variability plays some part, the preponderance of evidence indicates that human activities—particularly emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases—are mostly responsible for making our planet warmer.
Oppressively hot and humid air masses lingering over populated areas can produce many deaths, especially in the middle latitudes, where many people—including the very young, the very old, and those with health problems—may be more susceptible to heat stress. Notable modern episodes include the Russian heat wave of 2010 (which covered 1,036,000 square km [400,000 square miles] and killed 55,000 people), the European heat wave of 2003 (in which more than 30,000 people died), the U.S. heat wave and drought of 1988 (which killed more than 4,000 people), and the Indian heat wave of 2015 (which killed more than 2,500 people).
The human toll of escalating temperatures is stark and sobering. Heatwaves, exacerbated by climate change, have become more frequent and intense, posing severe health risks. Heat-related illnesses and fatalities are on the rise, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions. Additionally, the economic toll of extreme heat events, including decreased labor productivity and increased healthcare expenditures, is substantial.
Impact on Biodiversity
The impact of rising temperatures on biodiversity is profound, with ecosystems worldwide facing unprecedented threats. Species migration and distribution patterns are shifting as they attempt to adapt to changing climatic conditions. Coral reefs, vital marine ecosystems teeming with life, are under immense stress due to ocean warming, leading to mass bleaching events and widespread mortality. Similarly, terrestrial habitats are experiencing disruptions in plant and animal life cycles, jeopardizing the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Agricultural Challenges
Agriculture, the backbone of human civilization, is under siege from rising temperatures. Heat stress can diminish crop yields, reduce livestock productivity, and compromise food security. Regions reliant on predictable climatic patterns for agricultural planning are grappling with erratic weather phenomena, including droughts, floods, and prolonged heat waves, which disrupt farming practices and threaten livelihoods.
Health Impacts & Community Resilience
Climate change poses a significant public health threat, with extreme heat, humidity, and precipitation affecting vulnerable populations and increasing the risk of vector-borne diseases. Improving community resilience through climate adaptation strategies is essential to mitigating these risks.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the adverse effects of rising temperatures and curb further climate change, concerted efforts at the individual, community, and global levels are imperative. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Transition to Renewable Energy: Embrace clean, renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Energy Efficiency: Promote energy efficiency measures in transportation, industry, and buildings to minimize energy consumption and carbon emissions.
3. Reforestation and Afforestation: Expand forest cover through reforestation and afforestation initiatives to sequester carbon dioxide and enhance biodiversity.
4. Sustainable Agriculture: Adopt sustainable agricultural practices such as agroforestry, organic farming, and precision agriculture to enhance resilience to climate change and minimize environmental impact.
5. Climate Resilience Planning: Develop and implement climate resilience strategies at the local, national, and global levels to adapt to changing climatic conditions and minimize vulnerability to extreme weather events.
6. Education and Advocacy: Raise awareness about the impacts of climate change and empower individuals and communities to take action through education, advocacy, and grassroots initiatives.
The recent surge in global temperatures underscores the urgent need for action to combat climate change. By implementing sustainable practices, fostering resilience, and raising awareness, we can chart a path towards a more sustainable future. It is imperative that we act decisively and collectively to safeguard our planet for future generations.


