As the global community continues to grapple with pressing environmental and social challenges, companies are increasingly recognizing the need to integrate sustainability principles into their operations. One powerful way to achieve this is by embedding compliance with sustainability standards and regulations into the core values of an organization.
Understanding the significance of integrating compliance into organizational values requires a deeper exploration of the interplay between compliance, sustainability, and organizational culture.
The Foundation of Sustainability
At its essence, sustainability embodies the concept of meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability – often referred to as the triple bottom line. Compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and standards forms the bedrock of sustainable business practices, providing a framework for responsible conduct.
The Role of Compliance in Sustainability
Compliance serves as a mechanism for ensuring that organizations operate ethically, minimize their environmental footprint, and uphold social equity. By adhering to environmental regulations, such as emissions standards and waste management protocols, companies can mitigate their impact on the planet and contribute to conservation efforts. Similarly, compliance with labor laws and human rights standards promotes fair treatment of employees and stakeholders, fostering a culture of inclusivity and respect.
Integrating Compliance into Organizational Values
To truly embrace sustainability, organizations must go beyond mere adherence to regulations and embed compliance into their core values. By making compliance a fundamental aspect of organizational culture, companies can instill a sense of accountability, integrity, and ethical responsibility among employees at all levels. This cultural shift not only enhances corporate reputation and stakeholder trust but also drives long-term value creation and resilience.
Benefits of Integrating Compliance into Organizational Values
1. Risk Mitigation: A culture of compliance reduces the risk of legal violations, regulatory fines, and reputational damage, safeguarding the organization’s financial and operational stability.
2. Enhanced Reputation: Companies that prioritize compliance and sustainability are viewed more favorably by consumers, investors, and other stakeholders, leading to enhanced brand reputation and market competitiveness.
3. Innovation and Efficiency: Integrating compliance into organizational values fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement, driving efficiencies, and promoting responsible resource management.
4. Employee Engagement and Retention: Employees are more likely to feel proud of working for an organization that prioritizes ethical conduct and sustainability, leading to higher levels of engagement, job satisfaction, and retention.
5. Long-Term Sustainability: By aligning compliance with organizational values, companies can future-proof their operations, adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes, and contribute to the transition towards a more sustainable global economy.
Implementing Effective Compliance Strategies
Achieving successful integration of compliance into organizational values requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing leadership commitment, employee empowerment, and stakeholder engagement. Key steps in this process include:
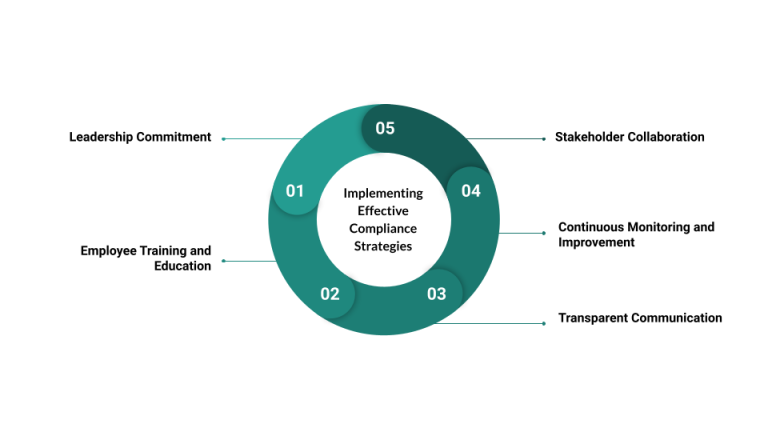
1. Leadership Commitment
Senior executives must champion the importance of compliance and sustainability, setting the tone for the entire organization and leading by example.
2. Employee Training and Education
Comprehensive training programs should be implemented to ensure that employees understand their responsibilities regarding compliance and sustainability standards.
3. Transparent Communication
Organizations should maintain open channels of communication to facilitate dialogue around compliance issues, encourage reporting of potential violations, and promote a culture of transparency and accountability.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Regular audits, assessments, and performance reviews should be conducted to evaluate compliance with relevant regulations and identify areas for improvement.
5. Stakeholder Collaboration
Collaboration with external stakeholders, including regulators, industry peers, and civil society organizations, can provide valuable insights and support in navigating complex compliance challenges.
Integrating compliance into organizational values is not only essential for achieving sustainability but also imperative for long-term business success. By embedding compliance with sustainability standards into the fabric of an organization, companies can foster a culture of responsibility, innovation, and resilience. As we navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected world, embracing compliance as a core value is not just a strategic choice – it’s a moral imperative in building a more sustainable future for generations to come.


