The world is facing a critical moment, dealing with rising waste, diminishing resources, and the pressing need to address climate change. The circular economy offers a compelling alternative, shifting from the conventional “take-make-dispose” model to one that prioritizes reuse, waste reduction, and the restoration of natural systems.
In 2024 and 2025, this approach has become even more vital as governments enforce stricter sustainability regulations, technologies like AI and IoT offer scalable solutions, and consumers demand greater transparency and eco-friendly practices. Understanding the principles of the circular economy is crucial—it’s an important step toward ensuring business resilience, promoting environmental sustainability, and encouraging societal progress.
Circular Economy Priority in 2024–2025
The circular economy (CE) offers a sustainable alternative to the traditional “take-make-dispose” approach of the linear economy. It is built on three key principles: eliminating waste and pollution from the design process, maximizing the use of materials through reuse, recycling, and refurbishment, and regenerating natural systems to help restore ecosystems.
The need to shift towards a circular economy (CE) is more pressing than ever. Shift beyond GDP and economic metrics to maximize human well-being, and prioritize the quality of life, equality, and happiness for all. As environmental challenges escalate, consumer preferences change and regulations evolve, CE has transformed from a mere idea into a crucial strategy for businesses, policymakers, and individuals. Here’s why the principles of the circular economy are becoming increasingly important in 2024 and 2025.
Tightening Sustainability Regulations
In 2024, governments are ramping up environmental regulations, highlighted by the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan, which emphasizes sustainable product design, waste reduction, and extended producer responsibility. Nations are also enhancing bans on single-use plastics, implementing recycling requirements, and enforcing carbon reduction strategies. Businesses that fail to comply may face fines, damage to their reputation, and limited access to markets.
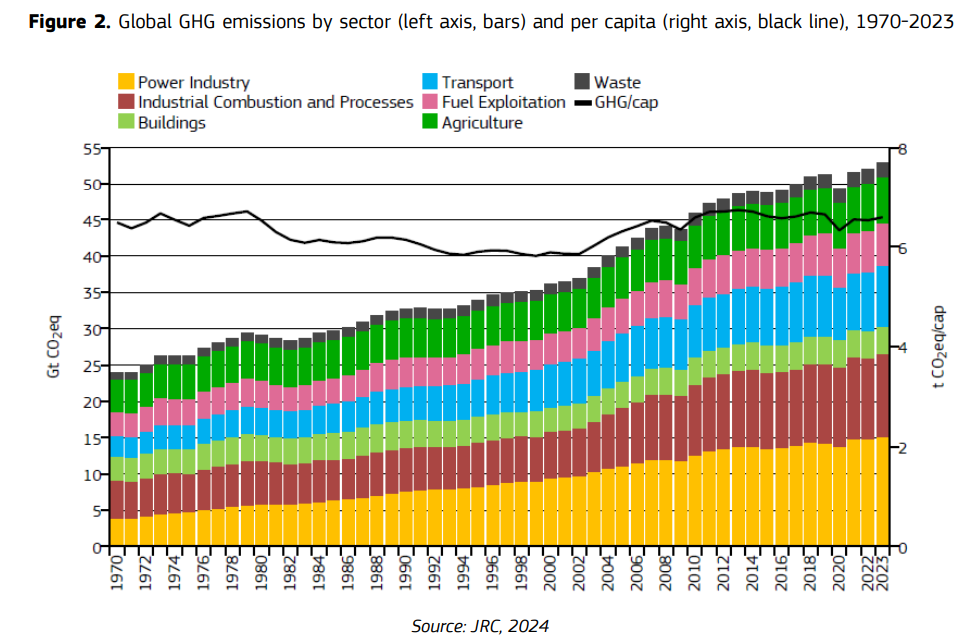
Addressing Climate Goals and Resource Scarcity
The circular economy supports global climate goals, including the net-zero targets of the Paris Agreement. By focusing on waste reduction, material reuse, and limiting resource extraction, the circular economy effectively lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the growing scarcity of resources, particularly rare earth metals, poses a significant challenge. Implementing circular strategies, such as recycling electronic waste and designing durable products, can help address these challenges, allowing businesses to thrive even in a future with limited resources.
Evolving Consumer Expectations
Modern consumers, especially younger generations, are placing a greater emphasis on sustainability and transparency. A study conducted in 2024 revealed that more than 70% of Millennials and Gen Z favor brands that implement eco-friendly practices. Circular economy models, including refillable packaging, repairable electronics, and second-life marketplaces, cater directly to these preferences. By embracing these strategies, companies not only lessen their environmental footprint but also foster deeper connections with eco-conscious consumers.
Advancements in Circular Technologies
Emerging technologies are making the shift to a circular economy more achievable and scalable than ever. For instance:
- AI and IoT enhance resource efficiency by enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing waste.
- Blockchain provides transparency in the supply chain, aiding in the tracking of materials and verifying sustainability claims.
- 3D printing facilitates localized, on-demand manufacturing, which helps decrease material waste and transportation emissions.
These innovations are empowering businesses to embrace circular economy principles while boosting operational efficiency and encouraging innovation.
Aligning with Global Sustainability Agendas
The global sustainability agenda is increasingly focused on circularity, as seen in initiatives like the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and various international frameworks addressing biodiversity and waste reduction. Circular Economy (CE) plays a crucial role in fulfilling SDG 12, which promotes responsible consumption and production, as well as SDG 13, which targets climate action. By adopting circular strategies, businesses and nations can support these important goals and improve their global reputation and competitiveness.
Benefits of Embracing Circular Economy Concepts
Adopting circular economy (CE) principles offers significant benefits to businesses, governments, and society as a whole. These benefits span environmental, economic, and social dimensions, making CE a key approach to creating a sustainable future.
Environmental Benefits
CE minimizes waste by keeping resources in use for as long as possible through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. For example, industrial symbiosis allows one company’s waste to become another’s resource, drastically reducing landfill contributions.
Economic Benefits
Companies that adopt CE models save costs by reusing materials, reducing their reliance on raw material extraction, and improving supply chains. For example, remanufacturing reduces manufacturing costs by 30–50% compared to creating products from scratch.
Social and Employment Benefits
CE models often rely on labor-intensive activities such as repair, recycling, and remanufacturing, which create jobs. Sustainability-focused consumers are drawn to brands that follow CE principles, such as repairable products or sustainable packaging. This strengthens brand trust and loyalty.
Business Resilience and Risk Management
CE reduces dependence on volatile raw material markets by reusing and recycling existing resources. For example, companies like Apple recover rare earth metals from old devices, reducing the risks of resource scarcity. With growing sustainability regulations, CE helps businesses meet legal requirements while avoiding fines and improving market access.
Aligning with Global Goals
CE policies align with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and SDG 13 (Climate Action). Organizations and nations that embrace circular economy practices are seen as frontrunners in sustainability, boosting their reputation and impact.
Adopting circular practices strengthens resilience, mitigates supply chain risks, and aligns with global sustainability goals like the UN SDGs. The shift to circularity is not just about preserving resources but also about reimagining how we produce, consume, and thrive. By prioritizing circular economy concepts today, we can create a sustainable, equitable, and prosperous future for generations to come. To learn more visit our Circular Economy course.


